Overview
Context
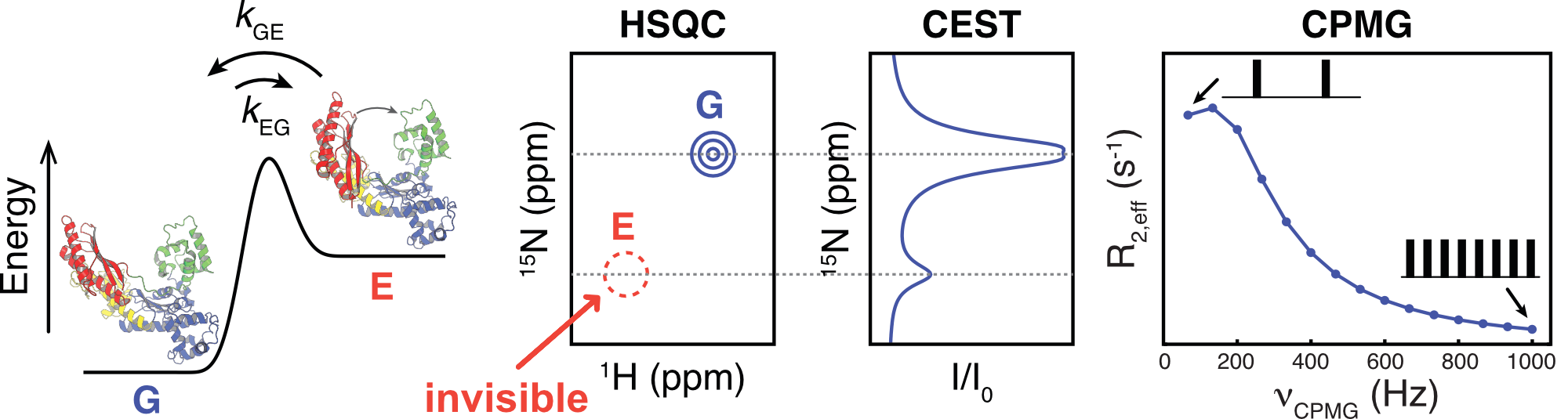
Biological macromolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, are intrinsically flexible, with their function (or dysfunction) often hinging on transitions between distinct conformational states. Understanding biomolecular function thus requires a quantitative characterization of their thermally accessible conformational landscapes. This task is challenging because many of the conformational states are transiently populated and exist at low concentrations, making them invisible to most conventional biophysical techniques. Over the past two decades, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) has emerged as a powerful tool for studying these elusive states at atomic resolution. Key to this success has been the development of chemical exchange-based approaches, such as Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) relaxation dispersion, R relaxation dispersion, and chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) experiments. These techniques, along with numerical tools, enable the extraction of kinetic (rates) and thermodynamic (populations) parameters associated with exchange processes, as well as structural information (chemical shifts) of sparsely populated, “invisible” excited states.
About ChemEx
ChemEx is an open-source Python application for the analysis of NMR chemical exchange data. It operates by integrating the evolution matrix of the spin system over the pulse sequence and extracting best-fit parameters through least-squares optimization. Because ChemEx does not rely on analytical equations to fit datasets, it can simulate virtually any type of experiment (e.g., D-CEST/COS-CEST) or kinetic model (e.g., 3-state exchange models) and account for most experimental details (e.g., finite pulse width, off-resonance effects). ChemEx provides a variety of pulse sequences and kinetic models to choose from, with main features including multi-step fits, joint analysis of datasets from different experiments, error analysis, and grid search. This documentation offers an overview of these features along with examples illustrating their use.
ChemEx is implemented in pure Python, leveraging established open-source libraries such as NumPy, SciPy, Matplotlib, Rich, and pydantic. The minimization process is powered by the LMFIT module, which includes multiple optimization algorithms available in SciPy.